Welcome to my comprehensive guide to SEO Troubleshooting, where I’ll help you overcome the most common search engine optimization problems that business owners face when managing their online presence.
From missing tags and duplicate tags to broken internal links and links with no follow tags, I’ll explain what all this jargon means, how such issues can negatively impact your website’s search engine ranking, and, more importantly, the actionable steps you need to take to fix them.
If you’ve noticed that your website’s traffic and rankings have been declining, or you’re just starting to optimize your site for search engines, this article is a must-read.
By the end of this guide, you’ll know exactly what to do to find and fix 15 of the most pressing technical, off-page, and on-page seo issues affecting your site.
SEO Troubleshooting: How to Fix Your Website
1. Missing Title Tags
Title tags, also known as title elements, are HTML tags used to specify the title of a web page. They are one of the main aspects search engine crawlers look at to understand what your content is about and which search terms to index it for.
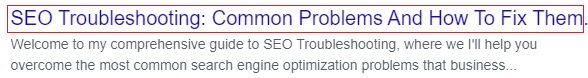
Perhaps more importantly, the title tag is responsible for displaying the title of your page in Google search results, making it essential for helping users decide whether to click through your content.
For example, I set the title tag of this page as “SEO troubleshooting: Common Problems and How to Fix Them” which is what you would’ve seen if you found this page in your search results.
A missing title tag can result in a poor user experience, as users may not be able to quickly identify whether your page meets their needs, and when neither users nor search crawlers know what your page is about, you’ll struggle to rank that content anywhere near the first page of search results for your targeted keywords.
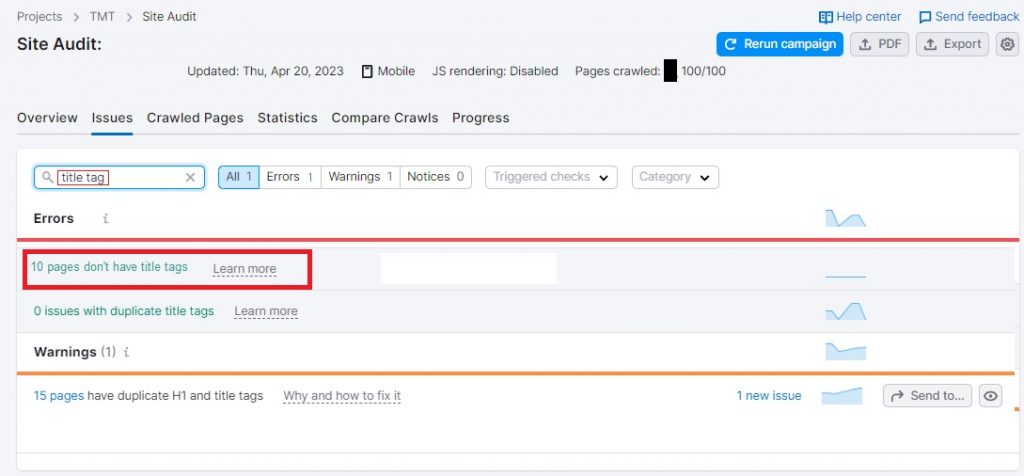
You can find missing tags on your website by running a site audit on popular SEO tools such as SEMRush.
To do this, just navigate to “Issues” and search for “title tag” to reveal how many of your pages are missing title tags. Clicking on this error message will show you precisely which pages you need to fix.
If your site runs on a popular CMS like WordPress or you manage using a website builder such as Wix, your title tag should be already generated from the main title on your page (H1), though most website platforms also offer a range of in-built tools and third-party extensions to help you add in missing title tags and optimize the ones that are underperforming.
2. Missing Meta Tags
Meta descriptions are those short blurbs that appear below the title in search engine results pages, giving users a quick preview of what your page is about.
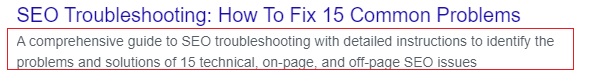
Not having them can lead to confusion and missed opportunities.
Without a meta description, search engines will often pull text from your page to use as a description. This can result in an unappealing or irrelevant snippet that doesn’t accurately reflect your content.
Additionally, a missing meta description can lead to a lower click-through rate, as users may not be enticed to click on your page if they don’t know what it’s about.
Missing meta descriptions occur when you forget to include this important information on your pages, something that’s easily done when you rush to get your new content out quickly.
Again, any of the SEO tools in this guide can help you identify missing meta descriptions in your site. All you have to to then is go back into your pages and take the time to craft unique and informative meta descriptions for each page on your website.
If you’re on WordPress, I recommend using either Yoast SEO or my personal favorite, RankMath, as these tools provide easy-to-use features for ensuring every page has the right metadata.
Given that every website platform is different, I recommend that if you’re not using WordPress, you search for “meta description” in your web builder’s help documentation for instructions on how to add them in.
Doing so can help improve your click-through rates and ensure that users have a clear understanding of what they can expect to find on your page. If you have a large website, you may want to prioritize adding meta descriptions to your most important or high-traffic pages first.
3. Duplicate Tags
Duplicate title tags are almost as big a problem as having no title tags at all.
Why?
Because search engines use title tags as a primary source of information about the content of a web page. If multiple pages on your website have the same title tag, how can a search crawler distinguish between the pages and understand which one to serve to users in response to relevant search terms?
Again, this can have a negative impact on your ability to appear in a high position (or possibly any position at all) in search results.
To fix duplicate title tags, use tools like the aforementioned SEMRush or Ahrefs Site Audit to find them.
To find duplicate title tags in Ahrefs Site Audit:
- Click on the “Site Audit” tab.
- Click on the “Content quality” report.
- Click on the “HTML tags” tab.
- Click on the “Bad duplicates” toggle.
- This will show you a list of pages with duplicate title tags.
Once you have identified the pages with duplicate title tags, you should create a different title tag for each page. Each title tag should accurately describe the content of the page and be unique to that page.
4. Missing Alt Tags
Missing alt tags should be high on your SEO checklist because they make it difficult for search engines and visually impaired users to understand the content of an image on a web page.
Alt tags provide a text description of the content of an image which can be read by screen readers, helping to improve your site’s accessibility and score brownie points from Google as a reward. They also give search crawlers more context about your site, which helps improve your rankings, so if you’re not using them, you need to fix that pronto.
AChecker is an excellent free tool that you can use to scan for accessibility issues on your website. If you have any missing alt tags, it will find them.

From there, it’s easy enough to add alt tags to images using your website builder.
In WordPress, for example, you can enter an alt-tag in the image uploader, or by viewing the Block options on the left-hand side of your editor and adding them in there.
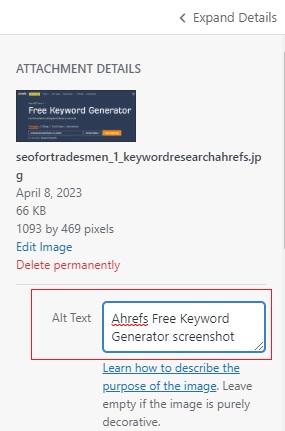
If you’re using Wix to build your website, you can enter missing alt-tags like this:
- Go to the page where you want to add the alt tag.
- Click on the image that you want to add the alt tag to.
- In the Image Settings section, enter a descriptive alt tag in the “What’s in the image? Tell Google” field.
For other website platforms, simply search the help files for “alt tags” to find instructions on what to do.
The alt text should be a concise and accurate description of the image, and it should include any relevant keywords related to the content of the image. For example, if you have an image of a red apple on your website, your alt tag could be “red apple”.
5. Broken Links
If you read my definitive guide to SEO for tradesmen, you’ll recall that broken links are a problem because they can negatively impact the user experience and SEO of your website.
When a user clicks on a broken internal link, they are directed to an error page instead of the intended content, which can be frustrating and lead to a high bounce rate. Broken internal can also negatively impact your website’s search engine ranking, as search engines may interpret them as a sign of low-quality or outdated content.
The good news is that although broken links are one of the most common search engine optimization problems people face, they’re also one of the easiest to fix.
The following tools can help you identify broken links on your site:
These tools will show which links aren’t working and where to find them on your website.
You can use this data to then go back into your website and either fix the link, replace it, delete it altogether, or redirect that link to another page.
Here are some ways to fix internal links with the “nofollow” tag:
6. Internal Links With No Follow Tags
“NoFollow” tags tell search engines not to follow the link or consider it when ranking the target page.
It used to be that webmasters would do this deliberately to focus all the link equity of a page on one link.
However, this is an ineffective and outdated practice, and it’s better to ensure that all of your internal links include a “DoFollow” tag, which distribute link equity throughout your website.
When you use dofollow tags, the search engines follow the link and attribute a portion of the page’s authority to the linked page. These tags also help search engine crawlers learn more about your website’s structure which can provide a further boost to your SEO.
The easiest way to identify and remove nofollow tags without using HTML is by using a browser extension that can highlight all nofollow links on a page. Here are the steps you can follow:
- Install a browser extension such as “NoFollow Simple” for Google Chrome or “NoFollow” for Firefox.
- Open the web page you want to check for nofollow links.
- Click on the browser extension icon to activate it.
- The nofollow links on the page will be highlighted, allowing you to easily identify them.
From there, you can log into your website and begin changing your links to do follow.
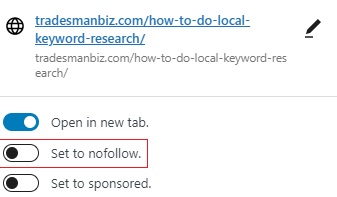
In WordPress, this is as simple as clicking on your hyperlinks and ensuring that “Set to NoFollow” is disabled.
While using dofollow for your internal links is generally a good idea, there are some instances where you may want to stick with nofollow.
For example, if you have a page with a lot of user-generated content, you may want to use the “nofollow” tag on links to external sites to avoid being penalized by search engines for spammy or low-quality content.
7. Negative or Poor-Quality Backlinks
Backlinks are one of the most important factors in determining a website’s search engine ranking. They signal to search engines that other websites consider your content to be valuable and authoritative. However, not all backlinks are created equal. Poor quality backlinks, or links from low-quality sites, can actually harm your SEO efforts.
The reason for this is simple: search engines are constantly updating their algorithms to ensure that they deliver the best possible results to their users. One of the ways they do this is by looking at the quality of the websites that are linking to your site. If a large number of low-quality sites are linking to your site, search engines may view this as an attempt to manipulate their algorithms and penalize your site accordingly.
So what can you do about poor quality backlinks? The first step is to identify them. You can use tools like Google Search Console or a third-party backlink analysis tool to identify any low-quality sites that are linking to your site. Once you have identified these sites, you can take steps to disavow them.
Disavowing a link means telling search engines that you do not want that link to be considered when calculating your site’s search engine ranking. You can do this by creating a disavow file and submitting it to Google Search Console.
It’s important to note that disavowing a link should be a last resort. If the link is from a site that is obviously spammy or malicious, then you should disavow it immediately. However, if the link is from a site that may have some value, but is not up to your standards, you may want to reach out to the site owner and ask them to remove the link. This can be a time-consuming process, but it can be worth it in the long run if it helps improve your site’s search engine ranking.
8. Orphan Pages
Orphan pages are pages on your website that are not linked to by any other pages on your site, making them difficult or impossible for users and search engines to find.
If a page is not linked to by any other pages on your site, it may be seen as unimportant or irrelevant by search engines and may not be indexed or ranked as highly in search results.
You can find orphan pages by going to the “Coverage” report in Google Search Console, and filtering by “Excluded” pages. This will show you a list of pages on your website that Google has indexed but is not linked to by any other pages on your site.
The simplest way to fix an orphan page is to add a link to it from another page on your site. This can help search engines discover the page and improve its visibility in search results.
As always, it’s important to ensure that the link is relevant and adds value to the user experience.
You can also benefit by locating your sitemap or, if you don’t already have one, creating one.
A site map is a file that lists all of the pages on your website, making it easier for search engines to crawl and index your site.
By including the orphan page in your sitemap, you can improve its visibility and increase the chances of it being discovered by search engines.
Other ways to prevent orphan pages disrupting your SEO gains include:
Improve Your Internal Linking
In addition to linking to the orphan page directly, you can also improve your internal linking strategy to ensure that all pages on your site are easily accessible. This can include adding links to related pages, using descriptive anchor text, and organizing your site architecture in a logical and intuitive way.
Remove The Page
If the orphan page is outdated, irrelevant, or not adding value to your site, it may be best to remove it altogether. This can help improve the overall quality and relevance of your site’s content, which can in turn improve your search engine rankings and user experience.
By fixing orphan pages on your website, you can improve the visibility and accessibility of your content, which can lead to increased traffic, engagement, and search engine rankings.
9. 404 Errors
Broken incoming links, also known as 404 errors, occur when a user clicks on a link that leads to a page that no longer exists or has been moved without a proper redirect.
If you’ve ever encountered a “404 Page Not Found” error on your website, you’ll know how frustrating they can be and what a negative impact they have on your experience with that website.
Naturally, you don’t want this to happen to your customers as, in all probability, they’ll simply leave your site and head to one of your competitors, signaling to Google that your site is of poor quality and little value.
The first step in troubleshooting your 404 errors is to find them in the first place.
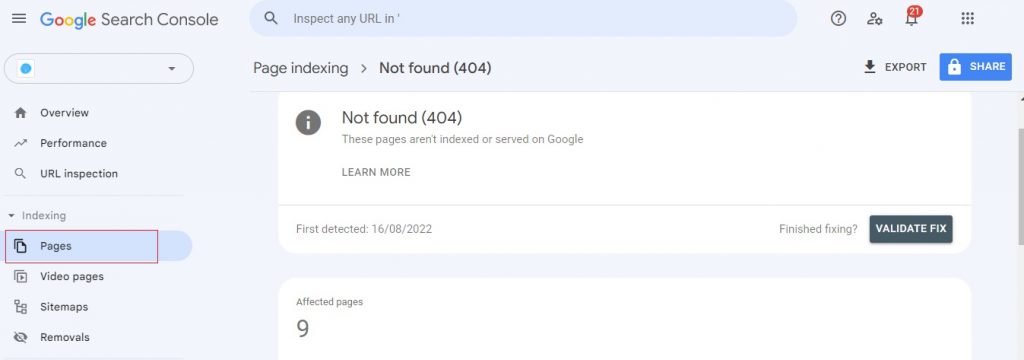
The easiest way to do this in Google Search Console.
Navigate to Pages – Why pages aren’t indexed, and select 404 errors.
The three most common causes of 404 errors are incorrectly typed URLs, deleted pages, or pages that have been moved.
If the link is pointing to a page that has been moved or renamed, update your links to reflect the new location of the page. This ensures that users and search engines can still access the content.
If the link is no longer relevant or useful, remove it from your site. This can help improve the overall quality of your site’s content and reduce the number of broken incoming links.
You can also redirect links to 404-producing pages so that they point to a working page on your site.
Finally, you can avoid mistyped URLs by keeping them short, simple, and easy to remember.
10. Slow Page Speeds
Slow page speed is a significant problem for websites because it can negatively affect user experience, search engine rankings, and, ultimately, website conversions. Here are some reasons why slow page speed is a problem:
Poor User Experience
Slow-loading pages can be frustrating for users, resulting in a negative user experience. Users are more likely to abandon a site that takes too long to load, which can lead to a decrease in website traffic and conversions.
Negative Impact on Page Rankings
Search engines take page speed into account when ranking websites. If your website takes too long to load, search engines may interpret this as a sign of low-quality content and poor user experience, which can result in a lower ranking.
Decreased Conversions
Slow page speed can significantly impact website conversions, meaning less people hiring your services. Studies have shown that even a one-second delay in page load time can result in a 7% decrease in conversions.
The good news is that site speed is such a common SEO problem for so many site owners that a wealth of tools have sprung up to tackle the problem.
As such, you don’t need any specialist technical knowledge to improve your site performance. Simply search for the appropriate tools for your website platform to help with all of the following site-speed-boosting tasks:
Optimize Images
Images are often the largest files on a webpage, and optimizing them can significantly reduce page load time. You can compress images to reduce their file size without sacrificing image quality.
Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A CDN can improve page load time by caching your website’s content on servers around the world, reducing the distance that content has to travel to reach users.
Minimize HTTP Requests
The more HTTP requests required to load a webpage, the longer it takes to load. Minimizing HTTP requests can significantly reduce page load time. This can be done by combining multiple files, such as CSS and JavaScript, into a single file.
Use Caching
Caching can significantly improve page load time by storing frequently accessed data on the user’s device or browser, reducing the amount of time it takes to load a page.
By implementing these solutions, you can improve your website’s page speed, resulting in a better user experience, higher search engine rankings, and increased website conversions.
11. Incorrect Hreflang Tag
Hreflang tags are used to indicate to search engines which language or regional version of a page should be served to users based on their location or language preferences. Incorrect hreflang tags can be a problem because they can confuse search engines, resulting in incorrect page indexing and ultimately lower search engine rankings. Here are some reasons why incorrect hreflang tags are a problem:
Here are some ways to fix incorrect hreflang tags:
Verify Hreflang Tags
Use Google Search Console or another SEO tool to verify your hreflang tags and make sure they are correct and properly implemented.
Use Language Codes
Use ISO language codes to indicate which language each page is written in.
Use Country Codes
Use country codes to indicate which version of a page should be served to users based on their location.
Use Canonical Tags
Use canonical tags to indicate the preferred version of a page, which can help prevent duplicate content issues.
By fixing incorrect hreflang tags, you can improve your website’s search engine visibility, provide a better user experience, and potentially increase website traffic and conversions.
12. Lack of HTTPS Encryption
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) encrypts the data that is sent between the user and the website, providing a secure connection. If your website is still using HTTP, it can create a host of problems, including damaging your website’s search engine optimization (SEO) efforts.
One of the most significant SEO problems associated with HTTP is that search engines like Google are increasingly favoring HTTPS websites over HTTP ones.
As a result, if your website is still using HTTP, it may suffer in search engine rankings, making it more difficult for potential customers to find your site. This can translate to a significant loss in traffic, leads, and sales.
What’s more, an HTTP site can be vulnerable to various types of cyber attacks, including man-in-the-middle attacks, where an attacker can intercept data transmitted between the user and the website.
If sensitive information, such as passwords or credit card details, are being transmitted, the attacker can potentially gain access to that information. This can lead to compromised data and loss of trust with your customers.
To fix this problem, you need to switch your website to HTTPS.
This involves obtaining an SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate and installing it on your website.
Most web hosting and domain companies offer SSL certificates, though you can also get a basic one for free from Let’s Encrypt.
Once you have done this, you will need to configure your website to use HTTPS by redirecting all HTTP traffic to the HTTPS version of your website.
This can be done using a variety of methods, including modifying your website’s .htaccess file or using a plugin if you are using a content management system (CMS) like WordPress.
13. Keyword Stuffing
Undoubtedly one of the most common SEO mistakes made by newcomers is keyword stuffing, which is the process of cramming as many related keywords into your content as possible with no regard for readability or relevance.
For example, let’s say you’re a handyman trying to rank higher on Google. You might use something like this:
“Are you in need of a handyman? Look no further than our handyman services. We offer the best handyman repairs, handyman maintenance, and handyman home improvement in the area. Our handyman team is dedicated to providing the best handyman services for all your handyman needs.”
That’s way too many handymen in one paragraph!
Sure, you’ve nailed all your primary and supporting keywords, but doing so makes your content sound spammy and unnatural.
Nobody wants to read a paragraph that repeats the same phrase over and over again. Plus, Google’s algorithms are designed to detect keyword stuffing, and if they catch you doing it, you could be penalized or even banned from search results.
So what can you do about it?
The solution is simple:
Write for your readers, not for search engines. Focus on creating high-quality, informative content that provides value to your audience.
Use keywords naturally and strategically, but don’t overdo it.
Aim for a keyword density of around 1-2%, and make sure your content flows smoothly and sounds like it was written by a human being, not a robot.
Remember, using the right keywords is important, but providing value to your readers and building trust and authority in your niche is even more important, so don’t ruin all your hard work by spamming site visitors with the same repetitive keywords.
14. Thin Content
Thin content is a term used when a page has very little useful or relevant content or just very little content at all.
For instance, you might create a page on your website that simply says “Handyman Services” and lists a few bullet points like “repairs” and “maintenance.” This type of thin content provides little value to your audience and doesn’t give search engines much information to work with.
The problem with thin content is that it can harm your search engine rankings, and it can also make it harder for potential customers to find you online. If your website is full of thin content, they may not be able to find the information they need, and they may not trust your business as a result.
So, how can you eliminate thin content from your SEO to-do list?
First, make sure that all the pages on your website provide value to your audience. Each page should have a clear purpose and offer useful information or solutions to your potential customers.
Second, make sure that each page has enough content to provide value and context. This doesn’t mean you should add unnecessary filler or fluff, but rather that you should make sure each page has enough information to be helpful and informative.
Finally, regularly review your website and remove any pages that are no longer relevant or useful. This will not only help you avoid thin content, but it will also make it easier for search engines and potential customers to find the information they need.
15. Site Isn’t Mobile Optimized
Saving one of the most important SEO problems til last, we come to the lack of mobile responsiveness. With more than half of all internet traffic now coming from mobile devices, it’s more important than ever to ensure that your website is optimized for mobile.
Search engines like Google have recognized this shift in user behavior and have updated their algorithms accordingly. Websites that are not optimized for mobile devices may be penalized in search engine rankings, leading to a decrease in traffic and potential customers.
Mobile optimization is about more than just having a responsive design that adapts to different screen sizes. It’s also about ensuring that your site’s content is easily accessible and readable on mobile devices. This means using larger fonts, minimizing the amount of scrolling required, and using clear, concise language.
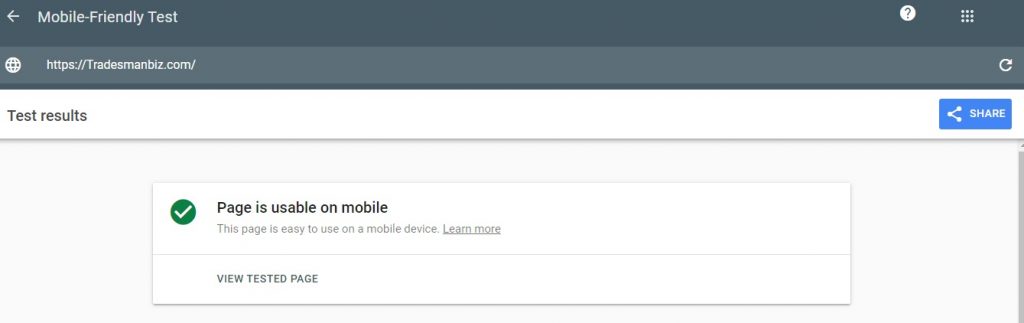
To ensure that your site is optimized for mobile devices, you can use tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test. This tool will analyze your site and provide recommendations for improving its mobile responsiveness.
In addition to improving your site’s SEO, mobile optimization can also improve the user experience for your visitors. Mobile users are often looking for quick, easy access to information, and a mobile-optimized site can help you deliver that.
Fixing Common SEO Problems: A Recap
SEO troubleshooting can be a complex and ongoing process, but understanding common problems and their solutions can greatly improve the visibility and performance of your website.
By identifying issues such as technical errors, content quality, and keyword optimization, you can implement effective strategies to enhance your search engine rankings and attract more organic traffic.
It’s important to regularly monitor your website’s SEO performance and adapt to changes in search engine algorithms to stay ahead of the competition. With a strategic approach and a commitment to ongoing improvement, you can overcome common SEO challenges and achieve long-term success for your website.
For more weekly advice on how to start, manage, and grow your business as a self-employed tradesperson or contractor, follow Tradesman Biz on Twitter, Facebook, or Linkedin.

Leave a Reply